Python中如何将脚本文件打包成可执行文件
June 26, 2015
Python中将脚本文件打包成可执行文件是如何来实现的呢?下面的内容将会通过具体的实例来演示Python中将脚本文件打包成可执行文件的实现方法及相关技巧:
将Python脚本文件包装成可执行文件,其目的有二:
一则: 不需要依赖Python编译器就可以运行软件
二则: 不想让自己的源码公布出去
常用的工具有: py2exe、cx_freeze等
【工具:py2exe】
安装py2exe
安装该工具很简单:
只需要从官方网站:http://www.py2exe.org/下载与版本对应的安装程序,点击下一步即可完成安装。
安装后,执行import py2exe,不报错则表示安装成功!
>>> import py2exe >>>
NOTE: 目前该工具只支持到Python2.7, 对于Python3而言,必须借助另外一个工具:cx_freeze
使用py2exe
第一步: 准备源代码,假如名为:Hello.py

第二步: 准备编译脚本,假如名为:setup.py
from distutils.core import setup import py2exe setup(windows=['Hello.py'])
第三步: 运行命令: setup.py py2exe
D:temp>setup.py py2exe

运行之后,会在我当前运行的目录下(D:temp)默认生成dict目录,里面的文件如下:
默认情况下,py2exe在目录dist下创建以下这些必须的文件:
1、一个或多个exe文件。如本例为: Hello.exe
2、python##.dll。 如本例中: Python27.dll
3、.pyd文件,它们是已编译的扩展名,它们是exe文件所需要的;加上其它的.dll文件,这些.dll是.pyd所需要的。
4、一个library.zip文件,它包含了已编译的纯的python模块如.pyc或.pyo
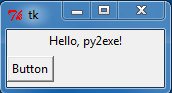
第四步: 双击Hello.exe可执行文件,跟源代码运行后同样的结果:
其他
1: 执行setup.py –help获取帮助信息
Global options:
--verbose (-v) run verbosely (default)
--quiet (-q) run quietly (turns verbosity off)
--dry-run (-n) don't actually do anything
--help (-h) show detailed help message
--no-user-cfg ignore pydistutils.cfg in your home directory
Options for 'py2exe' command:
--optimize (-O) optimization level: -O1 for "python -O", -O2 for
"python -OO", and -O0 to disable [default: -O0]
--dist-dir (-d) directory to put final built distributions in (default
is dist)
--excludes (-e) comma-separated list of modules to exclude
--dll-excludes comma-separated list of DLLs to exclude
--ignores comma-separated list of modules to ignore if they are
not found
--includes (-i) comma-separated list of modules to include
--packages (-p) comma-separated list of packages to include
--compressed (-c) create a compressed zipfile
--xref (-x) create and show a module cross reference
--bundle-files (-b) bundle dlls in the zipfile or the exe. Valid levels
are 1, 2, or 3 (default)
--skip-archive do not place Python bytecode files in an archive, put
them directly in the file system
--ascii (-a) do not automatically include encodings and codecs
--custom-boot-script Python file that will be run when setting up the
runtime environment
usage: setup.py [global_opts] cmd1 [cmd1_opts] [cmd2 [cmd2_opts] ...]
or: setup.py --help [cmd1 cmd2 ...]
or: setup.py --help-commands
or: setup.py cmd --help
2: 一个详细的编译脚本
# -*- coding: cp936 -*-
from distutils.core import setup
import py2exe
includes = ["encodings", "encodings.*"]
options = {"py2exe":
{"compressed": 1, # 压缩
"optimize": 2, # 优化级别
"ascii": 1, #
"includes":includes, # 编码方式
"bundle_files": 1 # 所有文件打包成一个zipfile或exe文件,有效级别1,2,3
}}
setup(
options=options, # 是否需要可选项,默认为None
zipfile=None, # 是否需要压缩像,默认为None
console=[{"script": "HelloCmd.py", "icon_resources": [(1, "pc.ico")]}], # 针对CMD控制端口
windows=[{"script": "HelloWin.py", "icon_resources": [(1, "pc.ico")]}], # 针对GUI图形窗口
data_files=[("magic",["App_x86.exe",]),],
version = "v1.01", # 版本信息
description = "py2exe testing",# 描述信息
name = "Hello, Py2exe", # 名字信息
)
Python中将脚本文件打包成可执行文件就是这样,欢迎大家参考。。。。
0 Comments